Cloud Hopper Cyber Espionage Campaign: Understanding the Chinese state-sponsored campaign targeting managed service providers.
The Cloud Hopper cyber espionage campaign stands as one of the most significant state-sponsored cyber threats, attributed to Chinese actors targeting managed service providers (MSPs) globally. This sophisticated operation aimed to infiltrate MSPs to gain access to their clients' networks, enabling espionage activities and intellectual property theft on a massive scale.
COMPANY OVERVIEW: The Cloud Hopper campaign, believed to be orchestrated by Chinese state-sponsored actors, specifically targeted MSPs, which provide IT infrastructure and support services to numerous organizations. By compromising MSPs, the attackers gained access to a vast network of clients, including government agencies, technology firms, and multinational corporations.
TIMELINE:
2016-2017: The Cloud Hopper campaign is first detected, with attacks targeting MSPs in various countries, including the United States, Europe, and Asia.
2018: The U.S. Department of Justice indicts Chinese nationals associated with the campaign, highlighting the extent of the threat and the involvement of state-sponsored actors.
2019: The campaign continues, with ongoing reports of cyber intrusions and data breaches linked to Chinese espionage activities.

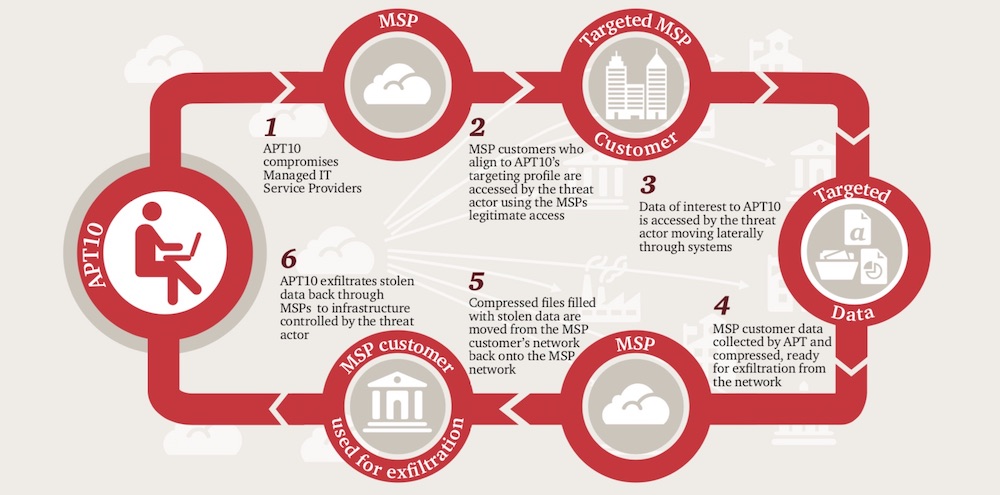
WHAT HAPPENED (Technical Detail): The Cloud Hopper cyber espionage campaign began with the initial compromise of managed service providers (MSPs), which serve as prime targets due to their extensive access to client networks. The attackers employed various tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to gain unauthorized access to MSP infrastructure, including spear-phishing emails, supply chain attacks, and exploiting vulnerabilities in software and systems.
Once inside the MSP network, the attackers conducted reconnaissance to identify high-value targets and establish persistence. They leveraged advanced malware, including custom-built tools and remote access Trojans (RATs), to maintain access and evade detection by security controls.
Through lateral movement within the MSP network, the attackers escalated privileges and sought out credentials and sensitive data belonging to MSP clients. They utilized compromised MSP accounts to pivot into client networks, exploiting trust relationships and weak security controls to expand their access and conduct reconnaissance.
Within client networks, the attackers conducted espionage activities, exfiltrating sensitive data, intellectual property, and other valuable information. They used encrypted communication channels and covert channels to conceal their activities and evade detection by security monitoring tools.
The Cloud Hopper campaign demonstrated a high degree of sophistication and coordination, indicative of state-sponsored cyber espionage. The attackers employed advanced evasion techniques, including fileless malware, living-off-the-land tactics, and anti-forensic measures, to bypass security controls and maintain stealthy access to compromised networks.
The campaign's technical complexity and scale posed significant challenges for detection and attribution. However, through collaborative efforts between cybersecurity researchers, government agencies, and industry partners, key indicators of compromise (IOCs) and TTPs associated with the campaign were identified, leading to enhanced detection capabilities and mitigation measures.
Despite efforts to disrupt the Cloud Hopper campaign, the threat posed by state-sponsored cyber espionage remains a persistent challenge for organizations worldwide. Continued vigilance, proactive security measures, and collaboration are essential to defend against such sophisticated threats and safeguard critical infrastructure and data assets.
IMPACT: The Cloud Hopper campaign had far-reaching consequences, compromising the networks of numerous organizations across multiple sectors. The attackers gained access to sensitive intellectual property, financial data, and government secrets, posing a significant threat to national security, economic stability, and corporate competitiveness.
MEASURES TAKEN BY VITIME COMPANY:
Enhanced Vendor Due Diligence: Vitime Company implemented rigorous vendor risk management processes, vetting and monitoring MSPs for security vulnerabilities and potential indicators of compromise.
Internal Security Controls: To mitigate the risk of supply chain attacks, Vitime strengthened its internal security controls, implementing measures such as network segmentation, least privilege access, and continuous monitoring for suspicious activity.
Threat Intelligence Sharing: Vitime actively participated in threat intelligence sharing initiatives, collaborating with industry peers, government agencies, and cybersecurity firms to exchange information and enhance collective defense efforts.
WHAT WE LEARNED:
Supply Chain Risks: The Cloud Hopper campaign underscored the vulnerability of supply chains to cyber attacks, highlighting the need for robust vendor risk management practices and heightened security controls.
State-Sponsored Threats: The involvement of Chinese state-sponsored actors in the Cloud Hopper campaign highlighted the persistent threat posed by nation-state adversaries and the importance of international cooperation in combating cyber espionage.
Continuous Vigilance: Organizations must maintain a proactive stance against evolving cyber threats, continuously assessing and improving their security posture to defend against sophisticated adversaries.
PERSONAL TAKEAWAY: The Cloud Hopper campaign serves as a stark reminder of the pervasive threat of state-sponsored cyber espionage and the critical importance of securing the global supply chain. As cybersecurity professionals, we must remain vigilant, collaborate with stakeholders, and leverage advanced technologies to detect and mitigate such threats effectively.
CONCLUSION: The Cloud Hopper cyber espionage campaign represents a significant challenge to global cybersecurity, targeting MSPs to gain access to a vast network of organizations and compromising sensitive data on a massive scale. However, through proactive security measures, international collaboration, and collective defense efforts, organizations can strengthen their resilience against state-sponsored cyber threats and safeguard critical assets and information.
