Facebook-Cambridge Analytica Data Scandal: Investigating the misuse of Facebook user data for political purposes.
The Facebook-Cambridge Analytica data scandal represents a watershed moment in the realm of data privacy and political manipulation. It exposed the unethical exploitation of Facebook user data by Cambridge Analytica, a political consulting firm, for targeted advertising and influence campaigns during the 2016 U.S. presidential election and other political contests worldwide.

COMPANY OVERVIEW: At the center of the scandal were Facebook, the social media platform with billions of users globally, and Cambridge Analytica, a now-defunct political consulting firm specializing in data analytics and behavioral microtargeting. The scandal highlighted the immense power wielded by tech companies and the potential for abuse in the collection and use of personal data for political purposes.
TIMELINE:
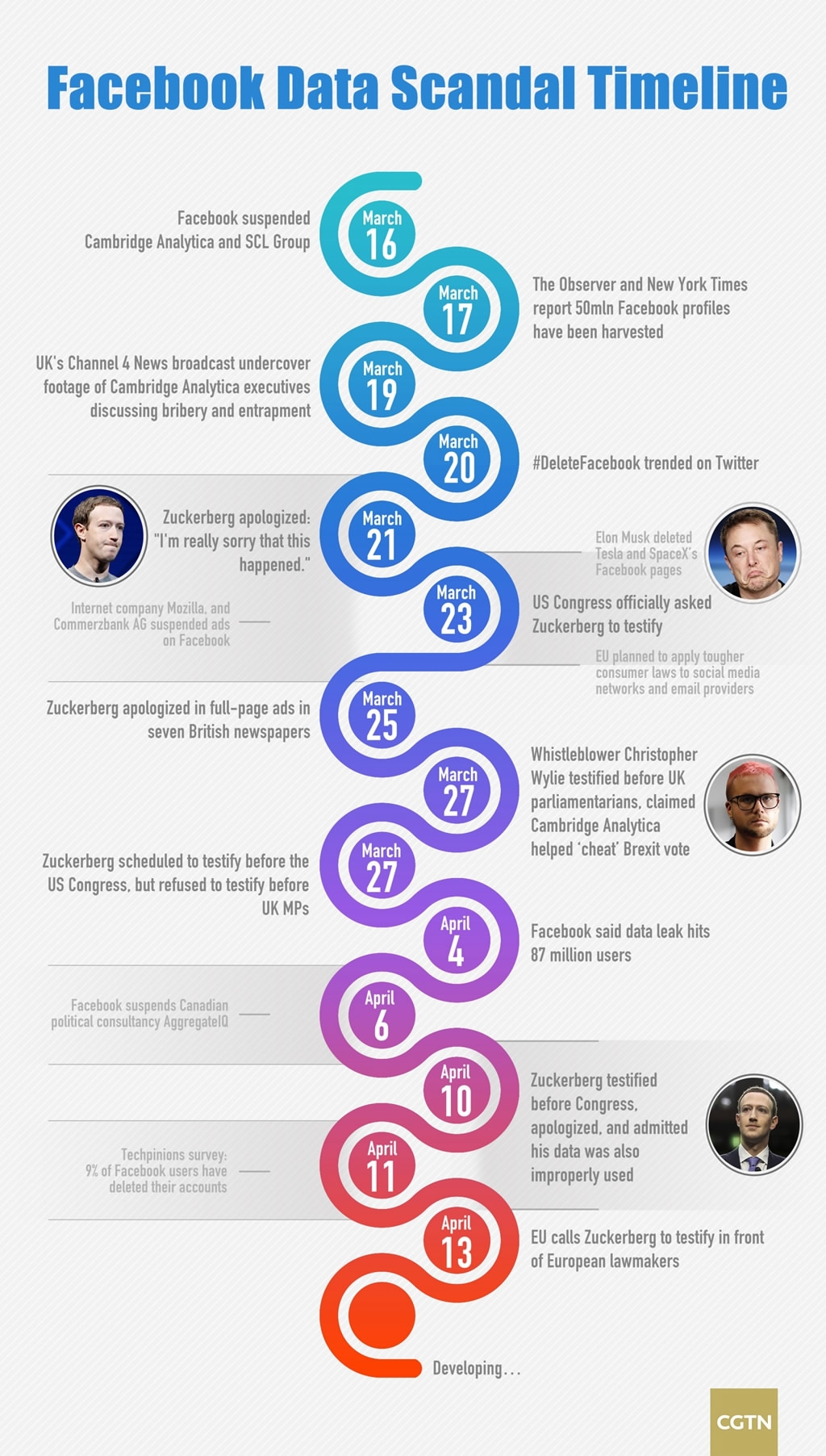
2013-2015: Cambridge University researcher Dr. Aleksandr Kogan develops a personality quiz app called "This Is Your Digital Life," which collects Facebook user data and that of their friends.
2014: Cambridge Analytica, working with Kogan, begins harvesting data from millions of Facebook users without their consent, leveraging the app's access to personal information.
2016: Cambridge Analytica provides data and targeted advertising services to political campaigns, including those of U.S. presidential candidate Donald Trump and the Brexit referendum in the UK.
2018: The scandal erupts when news reports reveal the extent of data misuse, prompting investigations by regulators and congressional hearings in the United States and the UK.
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/10480123/1.png)
IMPACT: The Facebook-Cambridge Analytica scandal had profound implications for data privacy, electoral integrity, and public trust in technology companies. It exposed the risks associated with the unchecked collection and sharing of personal data, raising concerns about manipulation, misinformation, and the erosion of democratic processes.
MEASURES TAKEN BY VITIME COMPANY:
Enhanced Data Privacy Controls: Victim Company implemented stricter privacy policies and data access controls, ensuring that user data is handled responsibly and transparently.
Third-Party Data Audits: Regular audits of third-party data providers were conducted to verify compliance with privacy regulations and ethical data practices.
User Education and Transparency: Victim Company prioritized user education initiatives, providing clear information about data collection practices and empowering users to control their privacy settings effectively.
WHAT HAPPENED (Technical Detail):
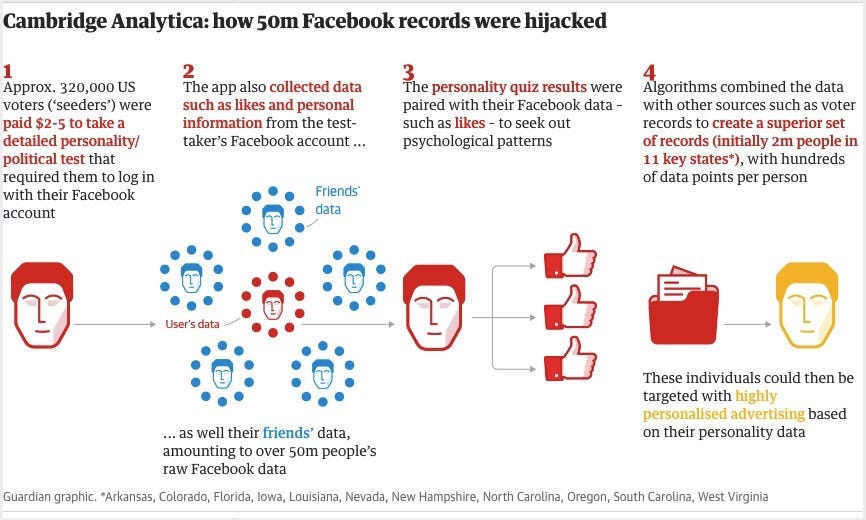
The Facebook-Cambridge Analytica scandal stemmed from the unauthorized harvesting of Facebook user data through a personality quiz app developed by Dr. Aleksandr Kogan, a researcher at Cambridge University. The app collected not only the data of users who installed it but also that of their Facebook friends, without their explicit consent.
Through the app, Kogan obtained a wealth of personal information, including demographic details, likes, and interactions, which were then shared with Cambridge Analytica for political targeting purposes. This data was used to build psychographic profiles of users, enabling highly targeted and personalized political advertising campaigns.
The data harvesting process exploited vulnerabilities in Facebook's platform at the time, allowing third-party developers to access extensive user data without adequate oversight or safeguards. This raised significant concerns about Facebook's data privacy practices and its responsibility to protect user information from exploitation and abuse.
In response to the scandal, Facebook implemented stricter data access policies, limiting the information accessible to third-party developers and conducting audits to identify and address potential misuse of user data. The incident prompted broader discussions about data privacy regulations, corporate accountability, and the ethical responsibilities of tech companies in the digital age.
CONCLUSION:
The Facebook-Cambridge Analytica data scandal was a watershed moment that exposed the vulnerabilities inherent in the digital ecosystem and the potential for abuse of personal data for political and commercial gain. It underscored the critical importance of robust data privacy regulations, transparent data practices, and corporate accountability in safeguarding user information and preserving democratic principles. The fallout from the scandal prompted significant reforms within Facebook and sparked broader discussions about the ethical responsibilities of technology companies, the need for regulatory oversight, and the protection of individual privacy rights in the digital age.
WHAT WE LEARNED:
Data Privacy Awareness: The scandal raised public awareness about the importance of data privacy and the risks associated with sharing personal information online. It highlighted the need for individuals to be vigilant about their digital footprint and to understand how their data may be collected, used, and shared by third parties.
Regulatory Reform: The scandal spurred calls for regulatory reform and greater oversight of tech companies' data practices. It underscored the need for comprehensive data privacy laws, such as the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), to protect user rights and hold companies accountable for data misuse.
Corporate Accountability: The incident emphasized the importance of corporate accountability and transparency in handling user data. It prompted tech companies to reevaluate their data policies, implement stricter controls over third-party access to user data, and improve transparency about data practices and privacy settings.
Ethical Data Use: The scandal highlighted the ethical implications of data collection and use, particularly in the context of political campaigns and influence operations. It prompted discussions about the responsible use of data for targeted advertising, the potential for algorithmic bias and manipulation, and the need for ethical guidelines to govern data-driven practices.
Public Trust: Ultimately, the Facebook-Cambridge Analytica scandal eroded public trust in technology companies and underscored the importance of earning and maintaining user trust through transparent and ethical data practices. It served as a stark reminder that safeguarding user privacy and upholding democratic values are essential pillars of a healthy digital society.

