LockBit Ransomware: Investigating the ransomware variant known for double extortion tactics.
Overview:

LockBit ransomware is a sophisticated threat known for its double extortion tactics, posing a grave risk to organizations globally. Emerging in 2019, it quickly gained notoriety for its encryption capabilities and the subsequent threats of data exposure unless ransom demands are met.
Company Overview:

LockBit operates as a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) model, with developers creating and maintaining the malware while affiliates distribute it. Affiliates are typically recruited from underground forums and employ various attack vectors such as phishing emails, exploit kits, and vulnerable remote desktop protocols (RDP) to infect target systems.
Timeline:
2019: LockBit is first observed in the wild, targeting organizations across diverse sectors.
Since its emergence, LockBit has been involved in numerous high-profile ransomware attacks, evolving its tactics and techniques to evade detection and enhance encryption capabilities.

Impact:
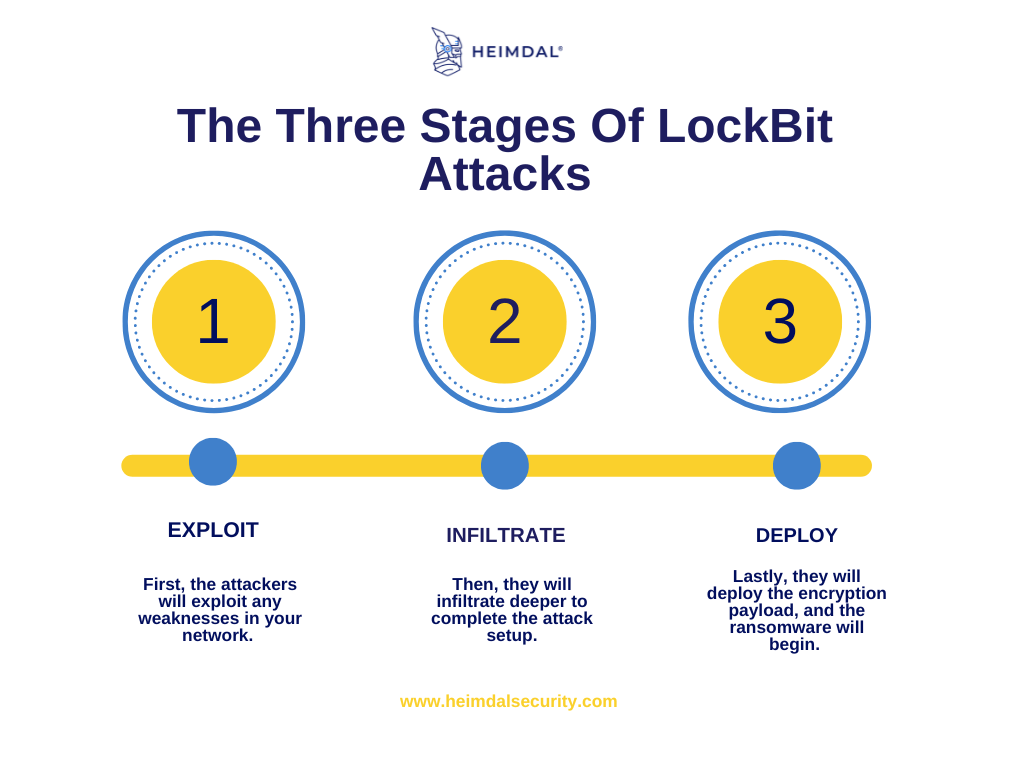
LockBit ransomware attacks have severe implications for victim organizations:
Financial Loss: Ransom payments, downtime, and recovery efforts result in substantial financial losses.
Operational Disruption: The encryption of critical data disrupts normal business operations, leading to productivity loss and service unavailability.
Reputational Damage: Public exposure of sensitive information tarnishes an organization's reputation and erodes customer trust, leading to long-term repercussions.
Measures Taken by Victim Company:
If Victim Company becomes a victim of LockBit ransomware, it would implement the following technical measures:
Incident Response Plan Activation: Immediate activation of the incident response plan to contain the attack and mitigate further damage.
Threat Detection and Analysis: Utilization of advanced threat detection tools and forensic analysis to identify the extent of the compromise and assess the ransomware's behavior.
Network Segmentation: Implementation of network segmentation to isolate infected systems and prevent lateral movement of the ransomware within the network.
Endpoint Protection: Deployment of endpoint protection solutions with behavioral analysis and machine learning capabilities to detect and block ransomware activity.
Backup and Recovery: Restoration of encrypted data from offline backups to minimize data loss and facilitate business continuity.
Threat Intelligence Sharing: Collaboration with industry peers and sharing threat intelligence to enhance defenses and mitigate future attacks.
What We Learned:
Analyzing the LockBit ransomware case provides critical technical insights:
Attack Vector Analysis: Understanding the attack vectors used by LockBit, such as phishing and RDP exploits, highlights the importance of patch management and security awareness training.
Encryption Mechanisms: Examining LockBit's encryption mechanisms underscores the need for robust data encryption and secure key management practices to thwart ransomware attacks.
Incident Response Best Practices: Implementing proactive incident response measures, including rapid detection, containment, and recovery, is essential to minimize the impact of ransomware attacks.
Personal Takeaway:
As a cybersecurity professional, studying the LockBit ransomware case reinforces the importance of continuous learning and technical proficiency. It emphasizes the need for up-to-date knowledge of ransomware tactics and countermeasures to effectively defend against evolving cyber threats.
Conclusion:
LockBit ransomware represents a significant technical challenge for organizations, requiring a multifaceted approach to defense. By understanding its technical intricacies and implementing proactive security measures, organizations can bolster their resilience and mitigate the risk of falling victim to ransomware attacks.
