Photo by Dan Meyers on Unsplash
Safeguarding Natanz: A Technical Deep Dive into Nuclear Fuel Enrichment Industrial Control System Security
Safeguarding Natanz: A Technical Deep Dive into Nuclear Fuel Enrichment Industrial Control System Security
In the realm of nuclear fuel enrichment, the security of industrial control systems (ICS) is paramount. Nowhere is this more evident than at Natanz, Iran's primary uranium enrichment facility. In this comprehensive analysis, we embark on a technical journey to explore the intricate layers of security surrounding Natanz's ICS, examining its evolution, vulnerabilities, and the measures taken to fortify its defenses.
Timeline:
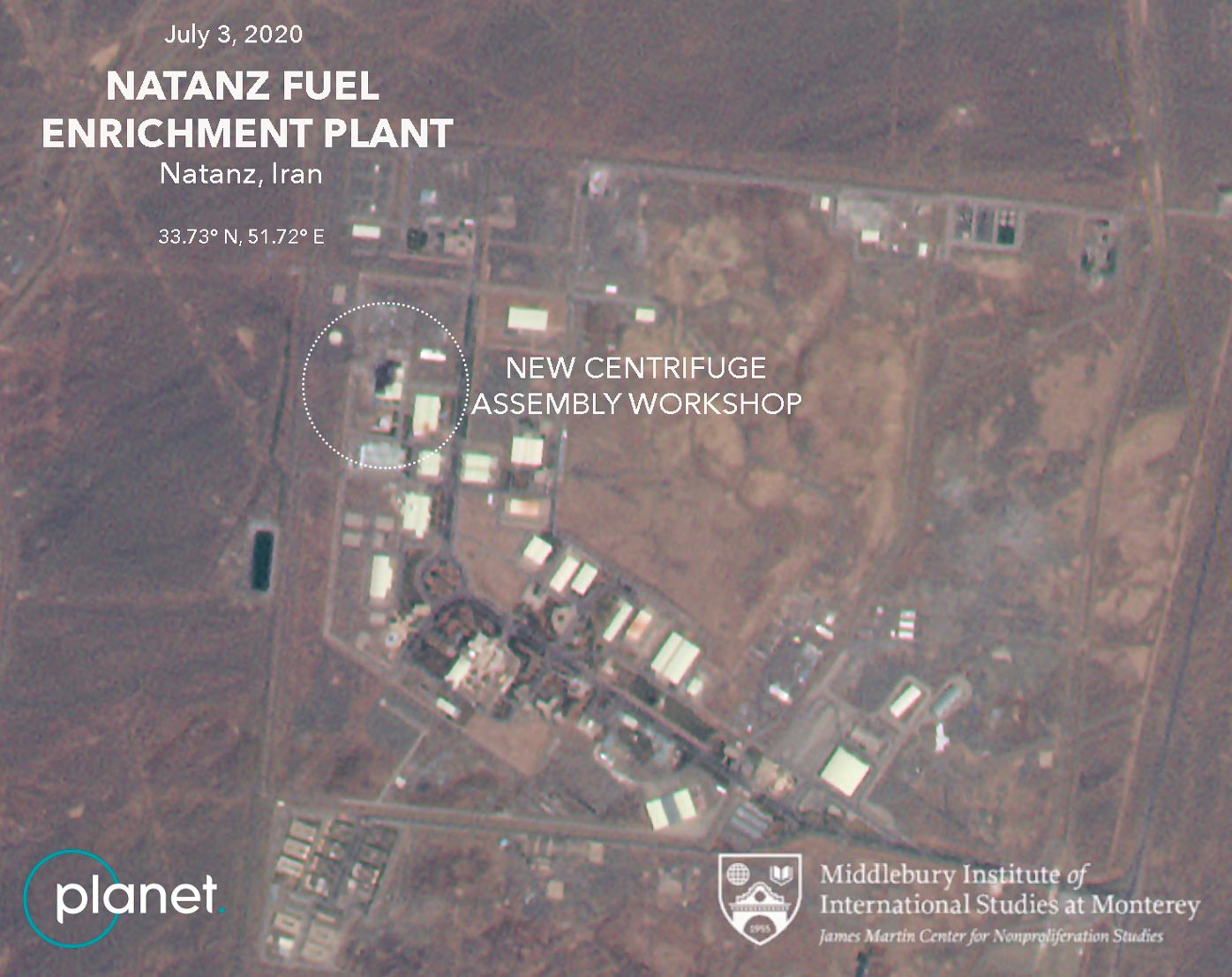
2002 - Natanz Facility Construction Begins: Construction of the Natanz uranium enrichment facility commences, marking a significant milestone in Iran's nuclear program.
2006 - Discovery of Stuxnet: The Stuxnet worm, a sophisticated cyber weapon designed to target industrial control systems, is discovered infecting systems worldwide. Subsequent analysis reveals its primary target: Natanz's centrifuge enrichment plant.
2007 - Stuxnet Targets Natanz: Stuxnet infiltrates Natanz's ICS, targeting Siemens programmable logic controllers (PLCs) used in centrifuge control systems. The attack disrupts operations and causes significant damage to centrifuge equipment.
2010 - Natanz Cybersecurity Overhaul: In response to the Stuxnet attack, Iran embarks on a comprehensive cybersecurity overhaul at Natanz, implementing stringent measures to protect its ICS from future cyber threats.
2015 - Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA): Iran agrees to limit its nuclear activities in exchange for sanctions relief under the JCPOA, leading to increased international scrutiny of Natanz's security measures.
2020 - Natanz Cyber Attack: A cyber attack targeting Natanz's ICS disrupts operations at the facility, causing a temporary shutdown of centrifuge enrichment activities. While the perpetrators remain unidentified, speculation abounds regarding potential state-sponsored involvement.
2021 - Natanz Security Upgrades: Iran announces plans to enhance security at Natanz, including the deployment of advanced intrusion detection systems, network segmentation, and enhanced access controls to safeguard its ICS against cyber threats.

Technical Insights:
Vulnerability Assessment: Conducting a comprehensive vulnerability assessment involves identifying and evaluating potential weaknesses in Natanz's ICS. This process includes assessing the susceptibility of control systems to various cyber threats, such as malware, insider threats, and supply chain risks. Vulnerability assessment tools and methodologies are employed to identify vulnerabilities in software, firmware, and hardware components used in the ICS infrastructure. By understanding these vulnerabilities, Natanz can prioritize remediation efforts and implement targeted security controls to mitigate potential risks.
Defense-in-Depth Strategies: Defense-in-depth is a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity that involves implementing multiple layers of security controls to protect Natanz's ICS from cyber threats. This includes:
Network Segmentation: Dividing the ICS network into separate segments or zones to contain the spread of cyber attacks and limit access to critical systems and assets.
Perimeter Security: Deploying firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and access control mechanisms at the network perimeter to prevent unauthorized access and detect suspicious activity.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Implementing IDS to monitor network traffic and detect potential cyber threats or anomalous behavior within the ICS environment.
Access Controls: Enforcing strict access controls and authentication mechanisms to restrict access to critical ICS components and ensure that only authorized personnel can interact with sensitive systems.
Patch Management: Effective patch management is crucial for maintaining the security of Natanz's ICS infrastructure. This involves regularly applying patches and updates to address known vulnerabilities in software, firmware, and operating systems used in the control systems. A robust patch management process includes:
Vulnerability Scanning: Regularly scanning Natanz's ICS environment for known vulnerabilities using automated vulnerability scanning tools.
Patch Deployment: Timely deployment of security patches and updates to address identified vulnerabilities and mitigate the risk of exploitation by cyber adversaries.
Change Management: Implementing change management processes to ensure that patches are thoroughly tested and validated before deployment to minimize the risk of system disruption or unintended consequences.
Security Awareness Training: Security awareness training is essential for educating Natanz personnel about cybersecurity best practices and raising awareness of potential threats and risks. This includes:
Phishing Awareness: Educating personnel about the risks of phishing attacks and providing training on how to identify and report suspicious emails or messages.
Social Engineering Awareness: Training employees to recognize and resist social engineering tactics used by malicious actors to manipulate individuals into disclosing sensitive information or performing unauthorized actions.
Access Control Policies: Reinforcing access control policies and procedures to ensure that employees understand their roles and responsibilities regarding access to Natanz's ICS infrastructure and data.

Conclusion:
The security of Natanz's nuclear fuel enrichment ICS remains a top priority in the face of evolving cyber threats and geopolitical tensions. By leveraging advanced cybersecurity measures, proactive threat intelligence, and international collaboration, Natanz endeavors to safeguard its critical infrastructure against potential cyber attacks, ensuring the stability and security of Iran's nuclear program for years to come.