Uber Data Breach: Understanding the 2016 breach and subsequent cover-up of stolen user data.

The Uber data breach of 2016 marks a significant incident in the realm of cybersecurity, involving the theft of sensitive user data followed by a subsequent cover-up by the company. This breach exposed critical flaws in Uber's data security practices and raised concerns about transparency and accountability in handling data breaches.
COMPANY OVERVIEW: Uber is a multinational transportation network company known for its ride-hailing services. With millions of users worldwide, Uber operates in numerous countries and handles vast amounts of sensitive user data, including personal information and payment details.
WHAT HAPPENED:
The Uber data breach of 2016 involved the unauthorized access and theft of sensitive user data followed by a subsequent cover-up by the company. Here's a detailed account of the events:
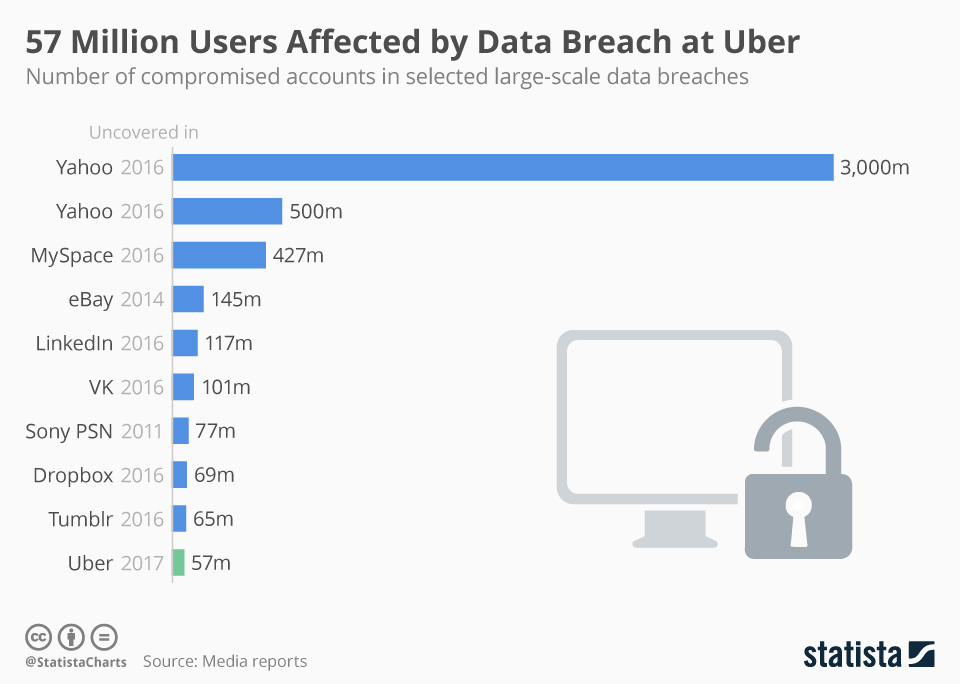
Data Theft: In late 2016, cybercriminals infiltrated Uber's systems and gained access to a significant amount of sensitive user data. The stolen data included the personal information of approximately 57 million Uber users worldwide, as well as the driver's license numbers of around 600,000 Uber drivers.
Discovery of the Breach: Uber discovered the data breach shortly after it occurred, with the company's security team detecting unauthorized access to its systems. The breach compromised a vast trove of user data, raising concerns about the security and integrity of Uber's platform.
Cover-Up Attempt: Instead of disclosing the breach to affected users, law enforcement agencies, or regulatory authorities, Uber opted to conceal the incident and keep it under wraps. In a controversial decision, Uber chose to pay the hackers $100,000 to delete the stolen data and refrain from disclosing the breach publicly.
Delayed Disclosure: The breach remained undisclosed to the public and regulators for over a year, with Uber failing to fulfill its obligation to report the incident in a timely manner. The company's failure to disclose the breach and its decision to pay off the hackers drew widespread criticism and raised serious ethical and legal concerns.
Public Disclosure: In November 2017, new Uber CEO Dara Khosrowshahi publicly disclosed the data breach, acknowledging the company's failure to handle the incident appropriately. The revelation sparked a firestorm of controversy and prompted regulatory investigations into Uber's data security practices and its handling of the breach.
Consequences: The Uber data breach had significant consequences for the company, including reputational damage, regulatory scrutiny, and legal repercussions. Uber faced fines and penalties for its failure to disclose the breach and for its attempts to cover up the incident, leading to further erosion of trust among users and stakeholders.
Overall, the Uber data breach of 2016 underscored the importance of transparency, accountability, and ethical behavior in cybersecurity incidents. It served as a stark reminder of the risks associated with data breaches and the imperative for companies to prioritize the protection of user data and uphold ethical standards in their response to security incidents.
TIMELINE:
Late 2016: Cybercriminals infiltrate Uber's systems and steal the personal information of approximately 57 million users and the driver's license numbers of around 600,000 drivers.
November 2016: Uber discovers the data breach but decides not to disclose it to affected users, law enforcement agencies, or regulatory authorities.
December 2016: Instead of reporting the breach, Uber pays the hackers $100,000 to delete the stolen data and keep the breach quiet.
November 2017: New Uber CEO Dara Khosrowshahi discloses the breach to the public and authorities, acknowledging the company's failure to handle the incident appropriately.
IMPACT: The Uber data breach had several significant impacts:
Compromised User Data: The breach exposed the personal information of millions of Uber users and drivers, including names, email addresses, phone numbers, and driver's license numbers. This put affected individuals at risk of identity theft and fraud.
Reputational Damage: Uber faced severe backlash from users, regulators, and the media for its failure to protect user data and its attempts to cover up the breach. The incident damaged Uber's reputation and eroded trust among its customers and stakeholders.
Regulatory Scrutiny: The data breach prompted regulatory investigations and legal actions against Uber, with authorities scrutinizing the company's data security practices and its handling of the breach. Uber faced fines and penalties for its failure to disclose the incident in a timely manner.
MEASURES TAKEN BY VITIME COMPANY: In response to the Uber data breach and to bolster its own cybersecurity measures, Vitime Company implemented several proactive measures:
Enhanced Data Protection: Vitime strengthened its data protection protocols, implementing robust encryption standards and access controls to safeguard sensitive user information.
Incident Response Plan: Vitime developed and tested an incident response plan to ensure a swift and effective response in the event of a data breach. This included procedures for incident detection, containment, mitigation, and notification.
Transparency and Accountability: Vitime prioritized transparency and accountability in its data security practices, committing to timely and transparent disclosure of any security incidents to affected users and regulatory authorities.
WHAT WE LEARNED:
Transparency is Key: The Uber data breach highlighted the importance of transparency and accountability in handling data breaches. Attempting to cover up breaches can exacerbate the damage and erode trust among users and stakeholders.
Prompt Disclosure: Prompt disclosure of data breaches is essential for enabling affected individuals to take necessary precautions and for regulators to investigate and mitigate the impact of the breach.
Ethical Considerations: Paying ransom to hackers, as Uber did in this case, raises ethical concerns and may incentivize further cybercrime. Companies should prioritize ethical considerations in their response to data breaches and refrain from engaging in illicit activities.
Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, is essential for organizations to avoid regulatory penalties and maintain the trust of their users.
PERSONAL TAKEAWAY: The Uber data breach serves as a cautionary tale about the importance of proactive cybersecurity measures, transparency, and ethical decision-making in handling data breaches. As cybersecurity professionals, we must prioritize the protection of user data, uphold ethical standards, and maintain transparency with stakeholders to build and preserve trust in our organizations.
CONCLUSION: The Uber data breach of 2016 underscores the critical importance of robust cybersecurity practices and transparent incident response procedures. By learning from past incidents and implementing proactive measures, organizations can strengthen their resilience to cyber threats and safeguard the integrity and trustworthiness of their platforms and services.
